Hundreds of millions of patients around the world are affected by health care-associated infections (HAI). Every day, HAI results in prolonged hospital stays, long-term disability, increased resistance of microorganisms to antimicrobials, massive additional costs for health systems, emotional and personal burden for patients and their family, and unnecessary deaths. To prevent HAI, it is important to identify their causes, understand how big the problem is, and evaluate whether interventions to reduce HAI are successful.
Please note: These materials were launched on 05/12/2022.
Language: English
Health topic
Course information
Hundreds of millions of patients around the world are affected by health care-associated infections (HAI). Every day, HAI results in prolonged hospital stays, long-term disability, increased resistance of microorganisms to antimicrobials, massive additional costs for health systems, emotional and personal burden for patients and their family, and unnecessary deaths. To prevent HAI, it is important to identify their causes, understand how big the problem is, and evaluate whether interventions to reduce HAI are successful.
Learning Objectives:
By the end of this course, you will:
- explain basic concepts of epidemiology and their application to HAI surveillance;
- describe how to plan the initial steps for HAI surveillance;
- describe how to assess surveillance of a target population;
- describe how to select surveillance outcomes;
- identify and use standardized HAI case definitions;
- describe the health care-associated infection (HAI) data collection process;
- identify sources of HAI surveillance data;
- explain different types of surveillance methodology for data collection;
- collect appropriate numerator and denominator data;
- explain the methods for assessing the quality of surveillance data;
- describe how surveillance data should be analysed;
- explain HAI risk stratification;
- interpret HAI infection rates;
- prepare a report for HAI surveillance;
- identify how to communicate surveillance information to various groups;
- describe objectives and elements of HAI surveillance evaluation; and
- describe the need for continuous improvement of surveillance systems.
Course duration: Approximately 3.5 hours.
Certificates: A Record of Achievement will be issued to participants who receive at least 70% on the post-test. You have an unlimited number of attempts to meet the threshold. Participants who receive a Record of Achievement can also download an Open Badge for this course. Click here to learn how.
Course contents
Part 1:
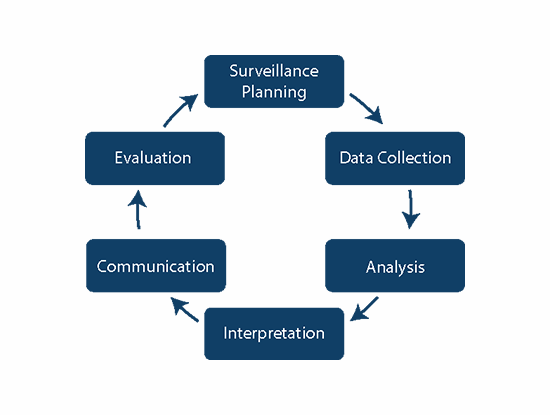
This first module on HAI surveillance will cover basic definitions, the epidemiology of HAI, and the steps for conducting surveillance.Part 2:
In the previous section, you learned about the first phase of surveillance: planning. In this module you will learn about the next few steps, namely data collection, analysis and interpretation.Part 3:
In this last part of the Health-Care Associated Infection (HAI) Surveillance module we will cover the remaining steps of conducting surveillance: communication, feedback and evaluation. You will learn how to prepare reports for different audiences and be able to identify who should know what information. HAI surveillance systems should have a built-in, regular process for evaluation of their management, efficiency and impact. This process should include evaluation of whether interventions are successful and the surveillance programme itself needs any adjustments.
Enroll me for this course
Certificate Requirements
- Gain a Record of Achievement by earning at least 70% of the maximum number of points from all graded assignments.
- Gain an Open Badge by completing the course.